Simulating a model
simulate.RmdReaction network models can be simulated as deterministic models or stochastic models. In this article we show the deterministic approach. An example of how to simualte from the stochastic model is available in this article.
Given a reaction network model, we can use the law of mass action to derive an ODE system that describes how the concentrations of the compounds in the system change in time.
To simulate the reaction network model deterministically with UQSA
you can use the simulator.c function:
simulate <- simulator.c(experiments = experiments, modelName = modelName, parMap = identity)This has created a closure
(simulate), with a single argument par:
sr <- simulate(par) # simulation resultsThe simulate function remembers the experiments that it
was created with and produces results of the same length as
experiments, in the same experimental conditions (e.g.,
same initial conditions).
It is often convenient to modify the parameters before passing them to the model. Here are possible reasons:
- the uncertainty is log normal
- you want to pass
exp(log(p) + rnorm(...))to the model rather thanpitself
- you want to pass
- the Markov chain is in log-space
- the sampler uses
p, but the model needs10^p
- the sampler uses
- the model parameters are linearly dependent
- we have to reliably pass
c(p[1]+p[2], p[2]+p[3], p[3]-p[1])to the model, every time
- we have to reliably pass
In such cases, you can write a mapping function, and use the
parMap argument-slot of simulator.c:
library(uqsa)
library(SBtabVFGEN)
f <- uqsa_example("AKAR4cl")
cl <- readRDS(uqsa_example("AKAR4cl",f="RDS"))
sb <- SBtabVFGEN::sbtab_from_tsv(f) # a list of data.frames
ex <- SBtabVFGEN::sbtab.data(sb,cl) # includes the data
parMap <- function(p){
return(exp(p))
}
modelName <- checkModel(comment(sb),uqsa_example("AKAR4cl",pat="_gvf.c$"))
sim <- simulator.c(ex,modelName,parMap)For example, here parameters are in log-space.
t <- as.numeric(ex[[1]]$outputTimes)
par <- log(sb$Parameter[["!DefaultValue"]])
np <- length(par)
stdv <- 0.2
REPS <- 50
P <- matrix(rnorm(np*REPS,mean=par,sd=stdv),np,REPS)
dim(P)
#> [1] 3 50
stm <- Sys.time()
sr <- sim(P)
#> <simpleError in dimnames(y[[i]]$state) <- list(names(experiments[[i]]$initialState), NULL, NULL): attempt to set an attribute on NULL>
etm <- Sys.time()
difftime(etm,stm)
#> <simpleError in dimnames(y[[i]]$state) <- list(names(experiments[[i]]$initialState), NULL, NULL): attempt to set an attribute on NULL>Now we sample trajectories associated with parameters in log-space:
T <- rep(c(t,NA),REPS) # the NA value will break the line
Z <- as.numeric(sr[[1]]$func[1,c(seq_along(t),NA),]) # at the end, so it doesn't loop
plot(T,Z,type='l',bty='n')
points(t,ex[[1]]$outputValues[[1]])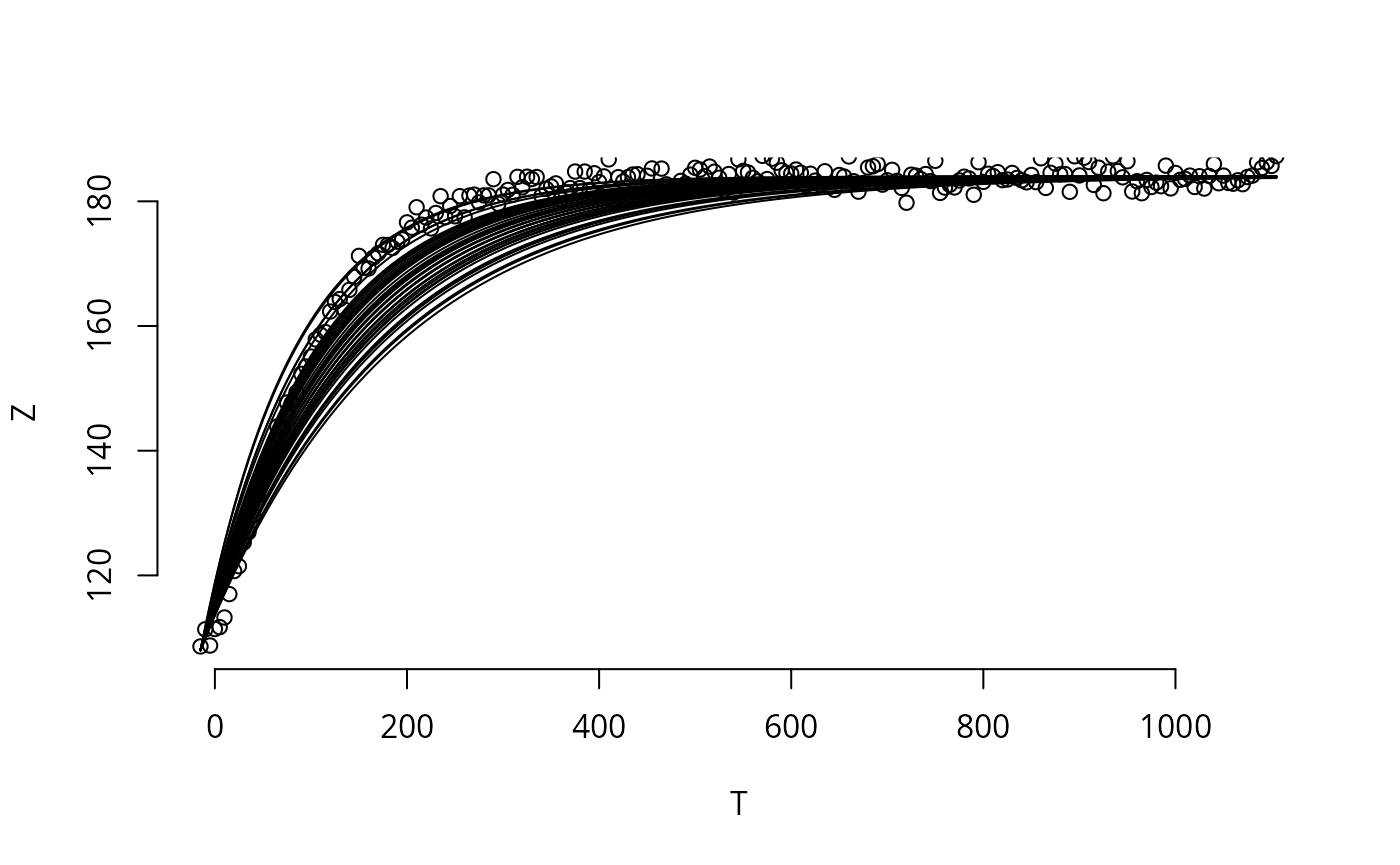
file.remove("AKAR4cl.so")
#> [1] TRUE